Inspecting 3D image data with pyclesperanto#
This notebook demonstrates how to navigate through 3D images.
import pyclesperanto_prototype as cle
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.io import imread
# Laod example data
input_image = imread('../../data/Haase_MRT_tfl3d1.tif')
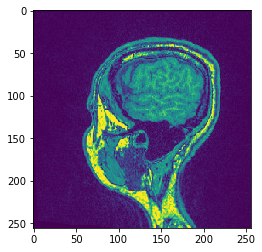
Copy Slice#
In order to visualize crop specific slices; without the image leaving GPU memory, use the copy_slice method.
# Copy Slice
image_slice = cle.create([256, 256]);
slice_z_position = 40.0;
cle.copy_slice(input_image, image_slice, slice_z_position)
# show result
cle.imshow(image_slice)
# Alternatively, don't hand over the output image and retrieve it
another_slice = cle.create_2d_xy(input_image)
cle.copy_slice(input_image, another_slice, slice_index = 80)
# show result
cle.imshow(another_slice)
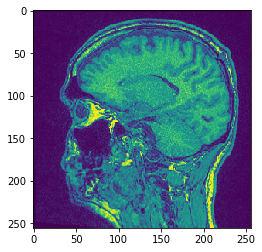
Projection#
pyclesperanto offers min/mean/max and sum projections in x, y and z.
# Maximum Z Projection
projection = cle.maximum_z_projection(input_image)
# show result
cle.imshow(projection)
If you pass an image stack to cle.imshow it will make the maximum intensity projection along Z for you:
cle.imshow(input_image)

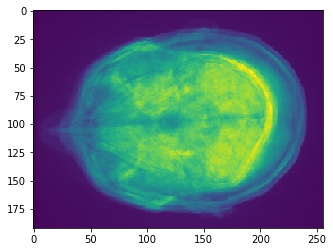
# Sum Z Projection
projection = cle.sum_z_projection(input_image)
# show result
cle.imshow(projection)
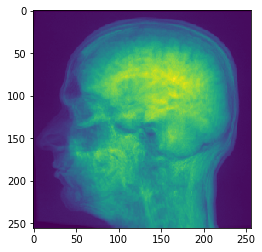
# Mean Y Projection
projection = cle.mean_y_projection(input_image)
# show result
cle.imshow(projection)
Transpose XZ#
In order to transpose axes of images in the GPU, use the transpose methods
# Transpose X against Z
transposed_image = cle.create([256, 256, 129]);
cle.transpose_xz(input_image, transposed_image)
# show result
cle.imshow(transposed_image[126])
cle.imshow(transposed_image[98])
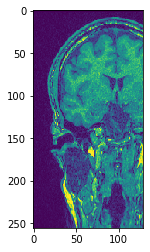
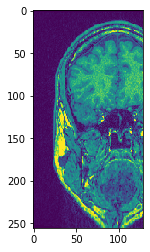
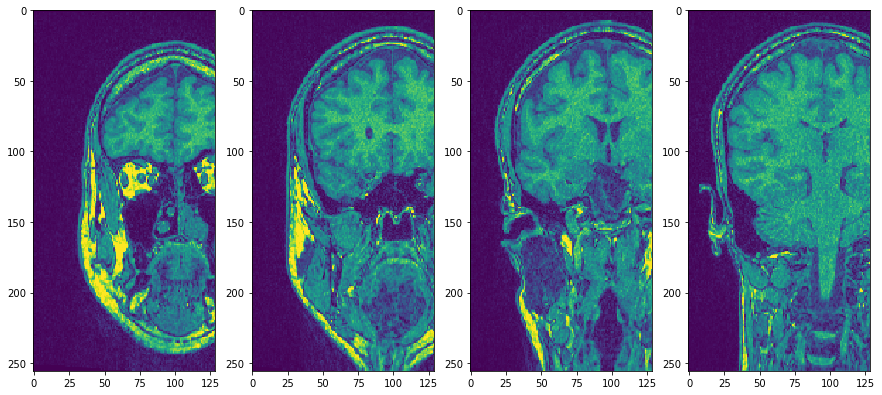
Use subplots to but them side by side
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(15, 7))
cle.imshow(transposed_image[75], plot=axs[0])
cle.imshow(transposed_image[100], plot=axs[1])
cle.imshow(transposed_image[125], plot=axs[2])
cle.imshow(transposed_image[150], plot=axs[3])